OPS proposal
Basics
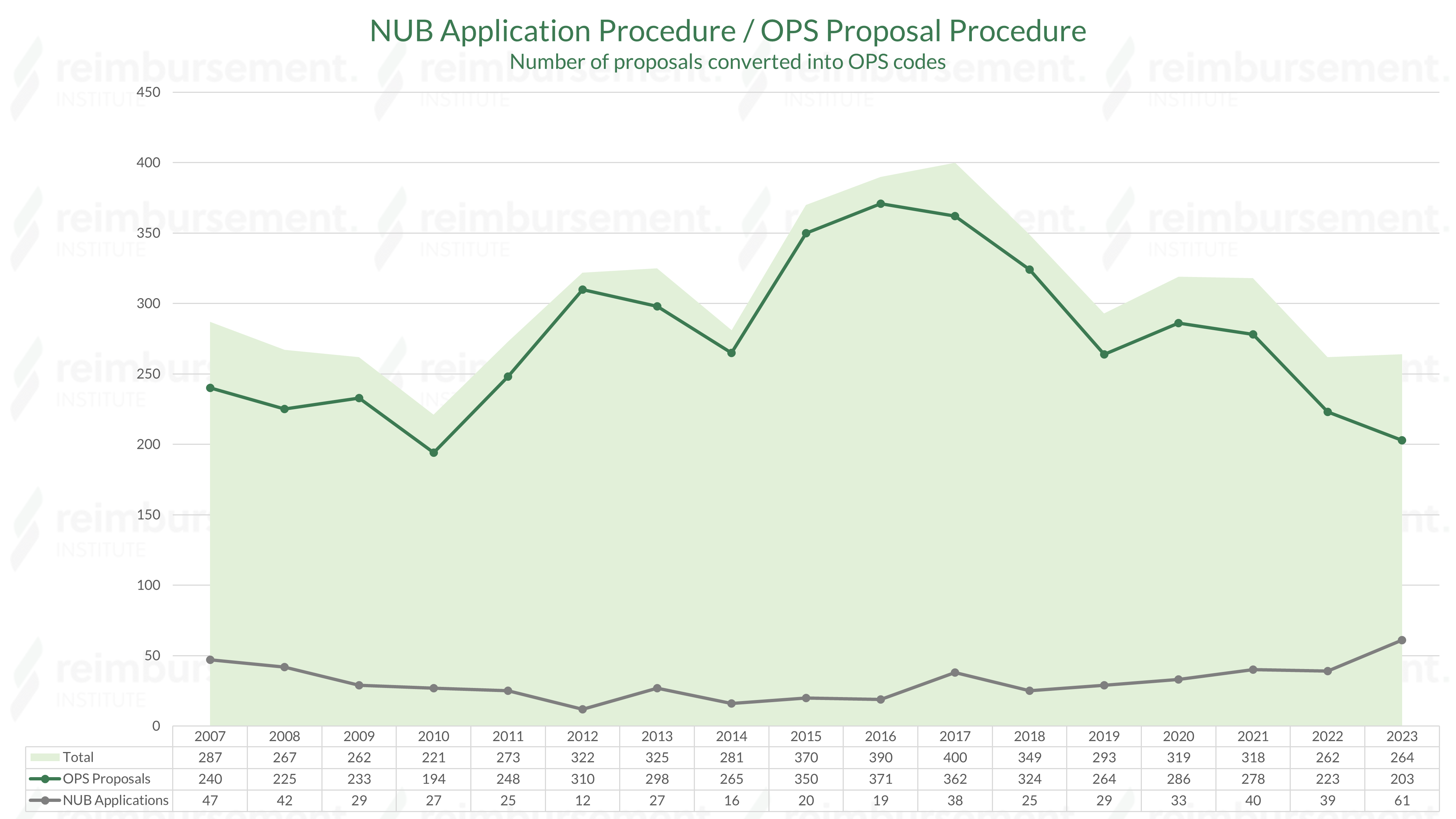
OPS proposal procedure
OPS proposal procedure
The OPS proposal procedure (or OPS application procedure) serves to provide external impetus for the need to differentiate existing OPS codes or to include a new one.
External impulse generation is important to point out deficiencies in code classification that do not automatically result from innovation funding via NUB or from the calculation procedure for DRG or ZE.
In addition to external impulses from professional associations or individuals, there is an internal need for further development of the OPS classification, which is addressed annually by the InEK to the BfArM. The BfArM is requested to create a coding capability for new or previously insufficient differentiated procedures in order to be able to collect data for costing.
⇒ Accordingly, it is not necessary to send out an OPS proposal to the BfArM for all procedures that have received a NUB status 1 or 11!
Submitting organizations
In particular, the medical societies are requested to submit a proposal (application) for further development, taking into account the economic or qualitative necessity and the aspects of the procedure. Thus, a professional evaluation and bundling of the proposals can be realized, which results in an identification of relevant proposals and thus contributes to an acceleration of the processing.
Individuals as well as submitting professional associations are asked to coordinate their proposals in advance with all or any other professional associations relevant to the proposal. For proposals that have not been coordinated with the professional associations responsible for the content, the BfArM will initiate this coordination process.
This coordination initiated by the BfArM may not be completed during the ongoing proposal process, so that the proposal cannot be implemented. Proposals concerning external quality assurance must be coordinated with the organization responsible for this (IQTiG).
Deadlines
The proposal procedure is opened at the beginning of December each year. The deadline for submission is always the last day of February of the following year (in leap year this is 29.02.).
Necessity of OPS
Operation and procedure codes are used to document the medical measures performed for a case of treatment in a hospital. This documentation serves a wide variety of requirements, which are found not only in economics but also, for example, in quality assurance, transparency, statistics, science and epidemiology.
Since the introduction of G-DRG and PEPP, the annual modification of the OPS classification has been focused on meeting these flat-rate payment systems. Thus, in addition to the other requirements mentioned above, the focus is primarily on billing purposes.
Operation and procedure codes can influence the assignment to a G-DRG and thus become economically relevant. Additional fees are also usually triggered by the documentation of an OPS.
The documentation of OPS codes by the service providers makes it possible to determine the number of names / operations per case as well as a case-related or DRG-related cost allocation. Among other things, this data is relevant for the adjustment of DRG information in relation to relative weight points. Complete documentation or use of existing OPS codes is of utmost relevance.